Join devRant
Do all the things like
++ or -- rants, post your own rants, comment on others' rants and build your customized dev avatar
Sign Up
Pipeless API

From the creators of devRant, Pipeless lets you power real-time personalized recommendations and activity feeds using a simple API
Learn More
Search - "password hashes"
-
I had a secondary Gmail account with a really nice short nickname (from the early invite/alpha days), forwarded to another of my mailboxes. It had a weak password, leaked as part of one of the many database leaks.
Eventually I noticed some dude in Brazil started using my Gmail, and he changed the password — but I still got a copy of everything he did through the forwarding rule. I caught him bragging to a friend on how he cracked hashes and stole and sold email accounts and user details in bulk.
He used my account as his main email account. Over the years I saw more and more personal details getting through. Eventually I received a mail with a plaintext password... which he also used for a PayPal account, coupled to a Mastercard.
I used a local website to send him a giant expensive bouquet of flowers with a box of chocolates, using his own PayPal and the default shipping address.
I included a card:
"Congratulations on acquiring my Gmail account, even if I'm 7 years late. Thanks for letting me be such an integral part of your life, for letting me know who you are, what you buy, how much you earn, who your family and friends are and where you live. I've surprised your mother with a cruise ticket as you mentioned on Facebook how sorry you were that you forgot her birthday and couldn't buy her a nice present. She seems like a lovely woman. I've also made a $1000 donation in your name to the EFF, to celebrate our distant friendship"31 -
Please for the love of god name your variables in a sensible way! How the FUCK am I supposed to read your shitcode if you decide to write 6 (!!!) nested loops with variables each named by exactly one character. With no comments whatsoever!
I would rather crack password hashes than this nonsense.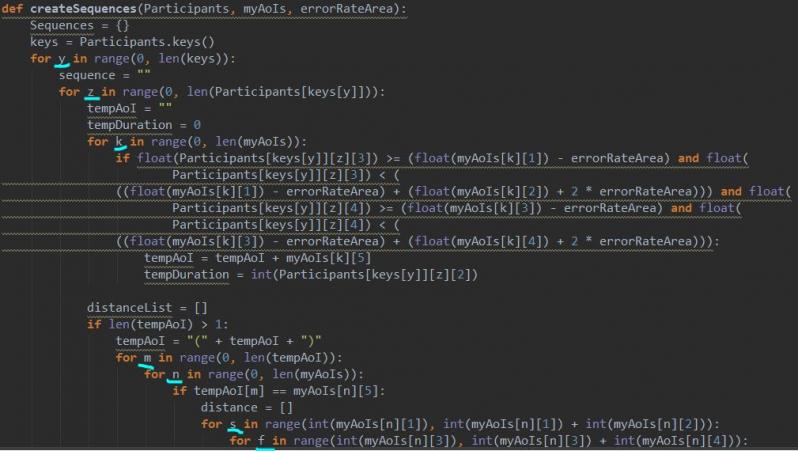 13
13 -
I'm fixing a security exploit, and it's a goddamn mountain of fuckups.
First, some idiot (read: the legendary dev himself) decided to use a gem to do some basic fucking searching instead of writing a simple fucking query.
Second, security ... didn't just drop the ball, they shit on it and flushed it down the toilet. The gem in question allows users to search by FUCKING EVERYTHING on EVERY FUCKING TABLE IN THE DB using really nice tools, actually, that let you do fancy things like traverse all the internal associations to find the users table, then list all users whose password reset hashes begin with "a" then "ab" then "abc" ... Want to steal an account? Hell, want to automate stealing all accounts? Only takes a few hundred requests apiece! Oooh, there's CC data, too, and its encryption keys!
Third, the gem does actually allow whitelisting associations, methods, etc. but ... well, the documentation actually recommends against it for whatever fucking reason, and that whitelisting is about as fine-grained as a club. You wanna restrict it to accessing the "name" column, but it needs to access both the "site" and "user" tables? Cool, users can now access site.name AND user.name... which is PII and totally leads to hefty fines. Thanks!
Fourth. If the gem can't access something thanks to the whitelist, it doesn't catch the exception and give you a useful error message or anything, no way. It just throws NoMethodErrors because fuck you. Good luck figuring out what they mean, especially if you have no idea you're even using the fucking thing.
Fifth. Thanks to the follower mentality prevalent in this hellhole, this shit is now used in a lot of places (and all indirectly!) so there's no searching for uses. Once I banhammer everything... well, loads of shit is going to break, and I won't have a fucking clue where because very few of these brainless sheep write decent test coverage (or even fucking write view tests), so I'll be doing tons of manual fucking testing. Oh, and I only have a week to finish everything, because fucking of course.
So, in summary. The stupid and lazy (and legendary!) dev fucked up. The stupid gem's author fucked up, and kept fucking up. The stupid devs followed the first fuckup's lead and repeated his fuck up, and fucked up on their own some more. It's fuckups all the fucking way down.rant security exploit root swears a lot actually root swears oh my stupid fucking people what the fuck fucking stupid fucking people20 -
Oh fuck, Germany wants to pull an Australia and force services-providers to disclose passwords, password-hashes,... to law enforcement.13
-
I'd never do anything "risky" in a prod environment if I considered it so at the time, but in retrospect there's *lots* of things considered risky now (both from a security and good practice viewpoint) that were standard practice not long ago:
- Not using any form of version control
- No tests (including no unit tests)
- Not considering XSS vulnerabilities
- Completely ignoring CSRF vulnerabilities
- Storing passwords as unsalted MD5 hashes (heck that was considered very *secure* in the days of plaintext password storage.)
...etc. I'm guilty of all of those previously. I daresay in the future there will be yet more things that may be standard practice now, but become taboos we look back on with similar disdain.1 -
PHP implicitely coercing password hashes to floats in comparisons is always a fun one
http://phpsadness.com/sad/4712 -
I was thinking about how I implement login functionality, and realised I have no clue how I came up with it so decided to ask if it was a good way to do things.
Basically, client logs in, username/email and pass are sent to server.
Server salts and hashes password and checks it against the one in the database for that user.
If its correct, send the client the user ID and the user token. (User id could be username, or a number, it depends)
When that client makes a request, the request must contain the ID and token.
The server checks that the ID and token combo are correct, and because the ID is linked to the user we know who it is and can complete the request.
Usually I make the token a random string of 16 or 32 chars, each account has their own token, and it may be stored in the browser so they stay logged in. I also normally add a "log out everywhere" button, which essentially just generates a new token to overrides the current one, making any previously saved tokens invalid.8 -
If I were to change all my passwords into hashes (so take a random word and hash it, ex 'table') and then use those on various websites, would people ever guess that my password is _an actual hash_ rather than a password in hashed form if they were to see it? Would such a meta-hash be safer if 'hackers' were to find it unencrypted?8
-
!rant
Just got a message from a recruiter. It was something different. There was a link with a ZIP file and a bunch of files in it. Plus two MD5 hashes. You should now find the correct private key and the encrypted message to decrypt it with the key. This gave you the password to get further in the application process.
Not particularly difficult, but a refreshing change from the usual blah blah.1 -
Hey there people, I have a few questions regarding neo4j. Your experience could also be very useful to me here @dfox.
1. Is neo4j good for storing user data, like password hashes, etc.. In addition to the regular relationships with other components of the ecosystem
2. Is neo4j good enough to accommodate a really large number of users..
3. Does DevRant use a dual database, like user info in Mongo and relationships like comments and ++ on neo4j or is it like everything on neo4j
For q.3, if you're not @dfox then just provide an idea of how you would handle the situation.7 -
I am trying to "invent" secure client-side authentication where all data are stored in browser encrypted and only accessible with the correct password. My question is, what is your opinion about my idea. If you think it is not secure or there is possible backdoor, let me know.
// INPUT:
- test string (hidden, random, random length)
- password
- password again
// THEN:
- hash test string with sha-512
- encrypt test string with password
- save hash of test string
// AUTH:
- decrypt test string
- hash decrypted string with sha-512
- compare hashes
- create password hash sha-512 (and delete password from memory, so you cannot get it somehow - possible hole here because hash is reversible with brute force)
// DATA PROCESSING
- encrypt/decrypt with password hash as secret (AES-256)
Thanks!
EDIT: Maybe some salt for test string would be nice8 -
I decided to run the ROCKYOU password list to see if there are any patterns in md5 hashing, not sure why but I am starting to confuse myself and I need a new pair of eyes to have a look.
in advance, sorry for the shitty image, that lappy is a temporary solution.
So the very accurate and not bias numbers show that the letter "0" appears more than the rest, would there be any use in let's say ordering the wordlist with words that have the most "0" and "7" in their hash to appear at the top?
I believe I might be trying to stretch the numbers and see a pattern where there is none but its worth a shot I think.
Note:
- These numbers come from only about ~14m words
My thinking trail is that if statisticaly these hashes are more likely to appear, they are more likely to be the one I am looking for? 3
3 -
Been wondering about something and can't figure out if I am a retard or a genius 😂.
If MD5 is so outdated and should not be used to store password hashes (let's say for whatever reason you cannot effectively switch to another algorithm) wouldn't it just be easier and more secure to just re-encrypt the hash again, so just MD5 the MD5 hash... in theory, wouldn't that make the hash virtually uncrackable because instead of trying to brute force actual real words, you now have a hash of essentially random characters which have no relation to the others, and even then, suppose you manage to crack the hash, you will get another hash to crack before getting to the password?5 -
Relatively often the OpenLDAP server (slapd) behaves a bit strange.
While it is little bit slow (I didn't do a benchmark but Active Directory seemed to be a bit faster but has other quirks is Windows only) with a small amount of users it's fine. slapd is the reference implementation of the LDAP protocol and I didn't expect it to be much better.
Some years ago slapd migrated to a different configuration style - instead of a configuration file and a required restart after every change made, it now uses an additional database for "live" configuration which also allows the deployment of multiple servers with the same configuration (I guess this is nice for larger setups). Many documentations online do not reflect the new configuration and so using the new configuration style requires some knowledge of LDAP itself.
It is possible to revert to the old file based method but the possibility might be removed by any future version - and restarts may take a little bit longer. So I guess, don't do that?
To access the configuration over the network (only using the command line on the server to edit the configuration is sometimes a bit... annoying) an additional internal user has to be created in the configuration database (while working on the local machine as root you are authenticated over a unix domain socket). I mean, I had to creat an administration user during the installation of the service but apparently this only for the main database...
The password in the configuration can be hashed as usual - but strangely it does only accept hashes of some passwords (a hashed version of "123456" is accepted but not hashes of different password, I mean what the...?) so I have to use a single plaintext password... (secure password hashing works for normal user and normal admin accounts).
But even worse are the default logging options: By default (atleast on Debian) the log level is set to DEBUG. Additionally if slapd detects optimization opportunities it writes them to the logs - at least once per connection, if not per query. Together with an application that did alot of connections and queries (this was not intendet and got fixed later) THIS RESULTED IN 32 GB LOG FILES IN ≤ 24 HOURS! - enough to fill up the disk and to crash other services (lessons learned: add more monitoring, monitoring, and monitoring and /var/log should be an extra partition). I mean logging optimization hints is certainly nice - it runs faster now (again, I did not do any benchmarks) - but ther verbosity was way too high.
The worst parts are the error messages: When entering a query string with a syntax errors, slapd returns the error code 80 without any additional text - the documentation reveals SO MUCH BETTER meaning: "other error", THIS IS SO HELPFULL... In the end I was able to find the reason why the input was rejected but in my experience the most error messages are little bit more precise.2

