Join devRant
Do all the things like
++ or -- rants, post your own rants, comment on others' rants and build your customized dev avatar
Sign Up
Pipeless API

From the creators of devRant, Pipeless lets you power real-time personalized recommendations and activity feeds using a simple API
Learn More
Search - "pastebin"
-
I really hate it when people asks for help on forums and mailing lists by taking a screen capture of code instead of pasting the text or using a gist or pastebin or any other USEFUL way to share code.2
-
Someone I work with transfered 7 credit card numbers including cvv and month/year using..... pastebin.
He was not signed in.3 -
Before a month I wrote I would like to create my own pastebin-like service.
And here it is... Pastitude!
End-to-end encrypted open-source service for sharing your awesome code :)
Tell me your opinions for this project in comments. Feel free to create an issue if you found any bug or have an idea how to improve Pastitude.
https://pastitude.com
GitHub link: https://github.com/PapiCZ/pastitude 16
16 -
So I built one of them Auto GPTs using Open Assistant and Python.
Essentially I have two chat rooms with each representing a different agent and some python written to facilitate the api communication and share messages between those two. Each agent is primed with a simple personality description, expected output format and a goal. I used almost identical inputs for both.
It boils down to "You are an expert AI system called Bot1 created to build a simple RPG videogame in python using pygame."
So anyway, I made that, and let it run for a couple of iterations and the results are just stunning, but not for the reasons you might expect. The short story is that they both turned into project managers discussing everything and anything *except* the actual game or game ideas and in the end they didn't produce a single line of code, but they did manage to make sure the project is agile and has enough documentation xD.
Presumably I need to tinker around with their personalities more and specify more well defined goals for this to lead to anything even remotely useful, but that's besides the point. I just thought others might find the actual conversation as funny as I did and wanted to share the output.
Here's a pastebin of the absolute madness they went through: https://pastebin.com/0Eq44k6D
PS: I don't expect anyone to read the whole thing word for word. Just scroll to a random point and check out the general conversation while keeping in mind that not a single line of code was developed throughout the entire thing8 -
On that day five years ago, Debian creator died under shady circumstances. His twitter was gone minutes after his last posts.
The lack of coverage, heck, the lack of basic awareness about death of THE CREATOR OF FUCKING DEBIAN is astonishing.
Twitter archive (the actual archived HTML) — https://archive.vn/OPlI7
Pastebin (raw tweets text) — https://pastebin.com/yk8bgru5
Goodnight, Ian. We miss you.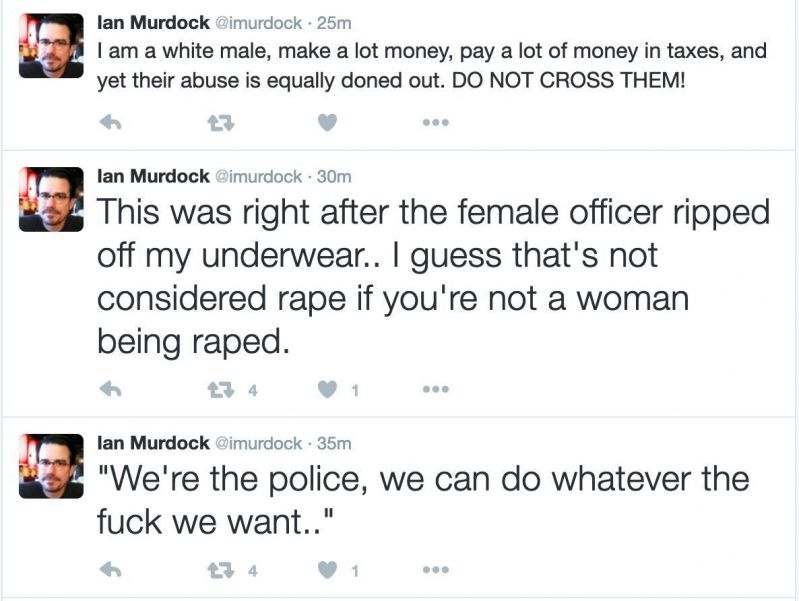 10
10 -
thankful for the new guy that handed me the opportunity to explain what the “cd” command does by linking him a pastebin that just says C DEEZ NUTS1
-
I'd like to create my own pastebin-like service...
So I'd like to ask which features do you miss (or hate) in these services?17 -
***ILLEGAL***
so its IPL(cricket) season in india, there is a OTT service called hotstar (its like netflix of india), the cricket streams exclusively on hotstar..
so a quick google search reveals literally thousands of emails & passwords, found a pastebin containing 500 emails&passwords ...but those are leaked last year most of passwords are changed & many of them enabled 2FA.. after looking through them we can find some passwords are similar to their emails , some contains birth year like 1975,1997 etc, some passwords end with 123 ..so after trying a few different versions of the passwords like
1) password123 -> password@123, password1234
2) passwordyear -> password@year
2) for passwords similar to emails, we can add 123 ,1234, @ etc
created a quick python script for sending login requests
so after like 30-40 mins of work, i have 7 working accounts
*for those who have basic idea of security practices you can skip this part
lessons learnt
1) enable 2FA
2) use strong passwords, if you change your password , new password should be very different from the old one
there are several thousands of leaked plaintext passwords for services like netflix,spotify, hulu etc, are easily available using simple google search,
after looking through & analysing thousands of them you can find many common passwords , common patterns
they may not be as obvious as password ,password123 but they are easily guessable.
mainly this is because these type of entertainment services are used by the average joe, they dont care about strong passwords, 2FA etc6 -
Localhost cloud in port 404 (C4)
Rogue like puzzle game (CF)
Piano tiles like runner game (CD)
Emotional Simulator (C7)
Pastebin client (PFW)
Updates in comments as i remember.6 -
Today, I had a small, but funny conversation with a person I knew from my education (application developing).
He suddenly asked, how to prevent using HTML-Tags in PHP.
So I send ihm following line:
$string = str_replace(array("<", ">"), array("<", ">"), $string);
Shortly after the line, he asked, how to add this into his query, which looks like:
$query = "INSERT INTO comments (name, email, quote, hinzugefuegt, ip_adress) VALUES ('" . $_POST['vName'] . "', '" . $_POST['eMail'] . "', '" . $_POST['q17'] . "', NOW(), '" . $_SERVER['REMOTE_ADDR'] . "')";
Now I thought: "Well, he don't even secure his variables", and I posted a Pastebin, which only "fixes" his issue with replacing the HTML-Tags, but still allows SQL injection.
https://pastebin.com/kfXGje4h
Maybe I'm a bad person, but he doesn't deserve it otherwise, because when I was still in education with him, I told him, he should learn to use prepared statements.3 -
Does anyone know of any tools for deobfuscating a batch script?
I got one of those scam emails with a .doc file attached and wanted to pull it apart, embedded in that file is a VBA script that runs as soon as the document is open. I have figured out how the script works I just have no idea when it comes to the batch script that its running, any help would be appreciated.
heres a pastebin link with the script, https://pastebin.com/SDWnQc4811 -
Heres some research into a new LLM architecture I recently built and have had actual success with.
The idea is simple, you do the standard thing of generating random vectors for your dictionary of tokens, we'll call these numbers your 'weights'. Then, for whatever sentence you want to use as input, you generate a context embedding by looking up those tokens, and putting them into a list.
Next, you do the same for the output you want to map to, lets call it the decoder embedding.
You then loop, and generate a 'noise embedding', for each vector or individual token in the context embedding, you then subtract that token's noise value from that token's embedding value or specific weight.
You find the weight index in the weight dictionary (one entry per word or token in your token dictionary) thats closest to this embedding. You use a version of cuckoo hashing where similar values are stored near each other, and the canonical weight values are actually the key of each key:value pair in your token dictionary. When doing this you align all random numbered keys in the dictionary (a uniform sample from 0 to 1), and look at hamming distance between the context embedding+noise embedding (called the encoder embedding) versus the canonical keys, with each digit from left to right being penalized by some factor f (because numbers further left are larger magnitudes), and then penalize or reward based on the numeric closeness of any given individual digit of the encoder embedding at the same index of any given weight i.
You then substitute the canonical weight in place of this encoder embedding, look up that weights index in my earliest version, and then use that index to lookup the word|token in the token dictionary and compare it to the word at the current index of the training output to match against.
Of course by switching to the hash version the lookup is significantly faster, but I digress.
That introduces a problem.
If each input token matches one output token how do we get variable length outputs, how do we do n-to-m mappings of input and output?
One of the things I explored was using pseudo-markovian processes, where theres one node, A, with two links to itself, B, and C.
B is a transition matrix, and A holds its own state. At any given timestep, A may use either the default transition matrix (training data encoder embeddings) with B, or it may generate new ones, using C and a context window of A's prior states.
C can be used to modify A, or it can be used to as a noise embedding to modify B.
A can take on the state of both A and C or A and B. In fact we do both, and measure which is closest to the correct output during training.
What this *doesn't* do is give us variable length encodings or decodings.
So I thought a while and said, if we're using noise embeddings, why can't we use multiple?
And if we're doing multiple, what if we used a middle layer, lets call it the 'key', and took its mean
over *many* training examples, and used it to map from the variance of an input (query) to the variance and mean of
a training or inference output (value).
But how does that tell us when to stop or continue generating tokens for the output?
Posted on pastebin if you want to read the whole thing (DR wouldn't post for some reason).
In any case I wasn't sure if I was dreaming or if I was off in left field, so I went and built the damn thing, the autoencoder part, wasn't even sure I could, but I did, and it just works. I'm still scratching my head.
https://pastebin.com/xAHRhmfH33 -
When I think my teachers can get any worse after sending me snippets of several Java classes in a single txt, one of them sent me SQL code of a full database dump in a Word document. 8 pages of SQL in its full glory!
I guess using the proper file extension/format or a service like PasteBin or GitHub Gist is way too advanced for them. -
This morning I was exploring dedekind numbers and decided to take it a little further.
Wrote a bunch of code and came up with an upperbound estimator for the dedekinds.
It's in python, so forgive me for that.
The bound starts low (x1.95) for D(4) and grows steadily from there, but from what I see it remains an upperbound throughout.
Leading me to an upperbound on D(10) of:
106703049056023475437882601027988757820103040109525947138938025501994616738352763576.33010981
Basics of the code are in the pastebin link below. I also imported the decimal module and set 'd = Decimal', and then did 'getcontext().prec=256' so python wouldn't covert any variable values into exponents due to overflow.
https://pastebin.com/2gjeebRu
The upperbound on D(9) is just a little shy of D(9)*10,000
which isn't bad all things considered.4 -
So I have seen this rant: https://devrant.io/rants/786219/... and I noticed that people said that they want to use the text for themselves. As you can't copy from the picture, here you go:
https://pastebin.com/zJnpSAHz2 -
After learning a bit about alife I was able to write
another one. It took some false starts
to understand the problem, but afterward I was able to refactor the problem into a sort of alife that measured and carefully tweaked various variables in the simulator, as the algorithm
explored the paramater space. After a few hours of letting the thing run, it successfully returned a remainder of zero on 41.4% of semiprimes tested.
This is the bad boy right here:
tracks[14]
[15, 2731, 52, 144, 41.4]
As they say, "he ain't there yet, but he got the spirit."
A 'track' here is just a collection of critical values and a fitness score that was found given a few million runs. These variables are used as input to a factoring algorithm, attempting to factor
any number you give it. These parameters tune or configure the algorithm to try slightly different things. After some trial runs, the results are stored in the last entry in the list, and the whole process is repeated with slightly different numbers, ones that have been modified
and mutated so we can explore the space of possible parameters.
Naturally this is a bit of a hodgepodge, but the critical thing is that for each configuration of numbers representing a track (and its results), I chose the lowest fitness of three runs.
Meaning hypothetically theres room for improvement with a tweak of the core algorithm, or even modifications or mutations to the
track variables. I have no clue if this scales up to very large semiprime products, so that would be one of the next steps to test.
Fitness also doesn't account for return speed. Some of these may have a lower overall fitness, but might in fact have a lower basis
(the value of 'i' that needs to be found in order for the algorithm to return rem%a == 0) for correctly factoring a semiprime.
The key thing here is that because all the entries generated here are dependent on in an outer loop that specifies [i] must never be greater than a/4 (for whatever the lowest factor generated in this run is), we can potentially push down the value of i further with some modification.
The entire exercise took 2.1735 billion iterations (3-4 hours, wasn't paying attention) to find this particular configuration of variables for the current algorithm, but as before, I suspect I can probably push the fitness value (percentage of semiprimes covered) higher, either with a few
additional parameters, or a modification of the algorithm itself (with a necessary rerun to find another track of equivalent or greater fitness).
I'm starting to bump up to the limit of my resources, I keep hitting the ceiling in my RAD-style write->test->repeat development loop.
I'm primarily using the limited number of identities I know, my gut intuition, combine with looking at the numbers themselves, to deduce relationships as I improve these and other algorithms, instead of relying strictly on memorizing identities like most mathematicians do.
I'm thinking if I want to keep that rapid write->eval loop I'm gonna have to upgrade, or go to a server environment to keep things snappy.
I did find that "jiggling" the parameters after each trial helped to explore the parameter
space better, so I wrote some methods to do just that. But what I wouldn't mind doing
is taking this a bit of a step further, and writing some code to optimize the variables
of the jiggle method itself, by automating the observation of real-time track fitness,
and discarding those changes that lead to the system tending to find tracks with lower fitness.
I'd also like to break up the entire regime into a training vs test set, but for now
the results are pretty promising.
I knew if I kept researching I'd likely find extensions like this. Of course tested on
billions of semiprimes, instead of simply millions, or tested on very large semiprimes, the
effect might disappear, though the more i've tested, and the larger the numbers I've given it,
the more the effect has become prevalent.
Hitko suggested in the earlier thread, based on a simplification, that the original algorithm
was a tautology, but something told me for a change that I got one correct. Without that initial challenge I might have chalked this up to another false start instead of pushing through and making further breakthroughs.
I'd also like to thank all those who followed along, helped, or cheered on the madness:
In no particular order ,demolishun, scor, root, iiii, karlisk, netikras, fast-nop, hazarth, chonky-quiche, Midnight-shcode, nanobot, c0d4, jilano, kescherrant, electrineer, nomad,
vintprox, sariel, lensflare, jeeper.
The original write up for the ideas behind the concept can be found at:
https://devrant.com/rants/7650612/...
If I left your name out, you better speak up, theres only so many invitations to the orgy.
Firecode already says we're past max capacity!5 -
1. I deleted Ubuntu and installed... you know, that one distro that everyone probably knows about... and whose name starts with a letter 'A'... and ends with 'h'. Now I'm trying to make it look nice.
2. I'm making a small Pastebin clone in Rust.10 -
Alright, it's time to play the guessing game.
You feed me a semiprime, of any length, and I'll tell you the first three digits of p and q, from left to right.
I get no hints besides the semiprime itself.
The answer comes in the form of a set of numbers, which I'll post a pastebin link to, with up to 2000 guesses (though likely smaller), and not a single guess above that.
If your pair of 3 digit numbers is present in that set, I win.
If not, you win.
Any takers?
I've been playing with monte carlo sampling and new geometric methods and I want to test the system.41 -
So I made a couple slight modifications to the formula in the previous post and got some pretty cool results.
The original post is here:
https://devrant.com/rants/5632235/...
The default transformation from p, to the new product (call it p2) leads to *very* large products (even for products of the first 100 primes).
Take for example
a = 6229, b = 10477, p = a*b = 65261233
While the new product the formula generates, has a factor tree that contains our factor (a), the product is huge.
How huge?
6489397687944607231601420206388875594346703505936926682969449167115933666916914363806993605...
and
So huge I put the whole number in a pastebin here:
https://pastebin.com/1bC5kqGH
Now, that number DOES contain our example factor 6229. I demonstrated that in the prior post.
But first, it's huge, 2972 digits long, and second, many of its factors are huge too.
Right from the get go I had hunch, and did (p2 mod p) and the result was surprisingly small, much closer to the original product. Then just to see what happens I subtracted this result from the original product.
The modification looks like this:
(p-(((abs(((((p)-(9**i)-9)+1))-((((9**i)-(p)-9)-2)))-p+1)-p)%p))
The result is '49856916'
Thats within the ballpark of our original product.
And then I factored it.
1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 12, 23, 29, 46, 58, 69, 87, 92, 116, 138, 174, 276, 348, 667, 1334, 2001, 2668, 4002, 6229, 8004, 12458, 18687, 24916, 37374, 74748, 143267, 180641, 286534, 361282, 429801, 541923, 573068, 722564, 859602, 1083846, 1719204, 2167692, 4154743, 8309486, 12464229, 16618972, 24928458, 49856916
Well damn. It's not a-smooth or b-smooth (where 'smoothness' is defined as 'all factors are beneath some number n')
but this is far more approachable than just factoring the original product.
It still requires a value of i equal to
i = floor(a/2)
But the results are actually factorable now if this works for other products.
I rewrote the script and tested on a couple million products and added decimal support, and I'm happy to report it works.
Script is posted here if you want to test it yourself:
https://pastebin.com/RNu1iiQ8
What I'll do next is probably add some basic factorization of trivial primes
(say the first 100), and then figure out the average number of factors in each derived product.
I'm also still working on getting to values of i < a/2, but only having sporadic success.
It also means *very* large numbers (either a subset of them or universally) with *lots* of factors may be reducible to unique products with just two non-trivial factors, but thats a big question mark for now.
@scor if you want to take a look.5 -
I have been working on idea similar to pastebin for mobile platform currently available on Android. The main concept is the easy share of Note in any language that is encrypted and the notes get deleted as soon as other party reads it. Plus you can encrypt it further by adding your own password and then share that password with others. This is useful when we are sharing our card details and other secret stuff with friends or family. The problem is that if you use mail or messaging stuff it gets stored in other party device and it can be exploited in future in case of theft or mobile loss. Here is my application for Android.
Please comment your reviews.,comments and suggestions here.
If you want to fork the code of both server and client comment that also.
https://play.google.com/store/apps/...7 -
Heres a fairly useless but interesting tidbit:
if i = n
then
r = (abs(((((p)-(9**i)-9)+1))-((((9**i)-(p)-9)-2)))-p+1+1)
then r%a will (almost*) always return 0. when n = floor(a/2) for the lowest non-trivial factor of a two factor product.
Thats not really the interesting bit though. The interesting bit is the result of r will always be some product with a *larger* factor tree that includes the factor A of p, but not p's other larger factor, B.
So, useless from what I can see. But its an interesting function on its own, simply because of what it does.
I wrote a script to test it. For all two-factor products of the first 1000 primes, (with no repeating combinations, so if we calculated say, 23*31, we skip 31*23), only 3262 products failed this little formula, out of half a million.
All others reliably returned 0 for the following..
~~~
i = floor(a/2)
r = (abs(((((p)-(9**i)-9)+1))-((((9**i)-(p)-9)-2)))-p+1+1)
r%a
~~~
The distribution of failures was *very* early on in the set of factors, and once fixed at the value of 3262, stopped increasing for the rest of the run.
I didn't calculate if some primes were more likely to cause a product to fail or not. Nor the factor trees, nor if the factor trees had any factors in common between products, or anything of that nature.
All in all I count this as a worthwhile experiment.
If you want to run the code yourself, I posted it to pastebin here:
https://pastebin.com/Q4LFKBjB
edit:
Tried wolfram alpha just to see what it says, but apparently not much. Wish it could tell me more.40 -
Not the 'most embarrassing' part but not my proud moment either.
My sir have recently put me alongside him as the teacher assistant in this summer's batch. Last week he had to go somewhere so he asked me to take a github session with the class( well not exactly asked, but i just voluntarily commented) . mind you am myself a novice, never done anything beyond pushing data commits and pull requests. (But sir was fine with it , saying he wants the students to atleast enough knowledgeable to submit there homeworks.)
Fast forward to Night before class and i am trying to sleep but couldn't. I had all ppts prepared, hell i even prepared a transcript( hell i uploaded it to pastebin thinking i will look at it and read ).
But worst shit always has to happen when you do a presentation.
When the class started, the wify was not working. Those guys had never had done anything related to it so first thing we did was to make sure every of them gets git installed(with lots of embarrassments and requesting everyone to share their hotspots.not my faluts, tbh).
Then again, am a Windows-linux user with noobie linux and null mac experience. So when this 1 girl with mac got problems installing, i was like, "please search on SO" 🐣 .
So after half an hour, almost everyone had their git/github accounts ready to work, so i started woth explaining open source and github's working. In the middle of session, i wanted to show them meaning of github's stars ("shows how appreciated a repo is"), nd i had thought of showing them the react js repo . And when i tried searching it i couldn't find it (its name is just react, not reactjs ) so ,again :🐥🐥🐣
So somehow this session of 1-1.5 hour got completed in 4 hours with me repeating myself many many many times.
And the most stupid thing: our institute has every session recorded, so my awkward presentation is definitely in their computers 🐣🐣🐥🐥



